使用PyQt6构建一个snake game
from PyQt6.QtCore import Qt, QTimer
from PyQt6.QtGui import QColor, QPainter
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow
CELL_SIZE = 30
GRID_SIZE = 20
SNAKE_INITIAL_LENGTH = 3
SNAKE_INITIAL_POSITION = (GRID_SIZE // 2, GRID_SIZE // 2)
SNAKE_INITIAL_DIRECTION = Qt.Key.Key_Right
FOOD_COLOR = QColor(0, 255, 0) ## Green color
class SnakeGame(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("Snake Game")
self.setFixedSize(CELL_SIZE * GRID_SIZE, CELL_SIZE * GRID_SIZE)
self.snake = [(SNAKE_INITIAL_POSITION[0], SNAKE_INITIAL_POSITION[1] + i) for i in range(SNAKE_INITIAL_LENGTH)]
self.direction = SNAKE_INITIAL_DIRECTION
self.food = self.generate_food()
self.timer = QTimer()
self.timer.timeout.connect(self.move_snake)
self.timer.start(200) ## Snake movement speed
def paintEvent(self, event):
painter = QPainter(self)
painter.setRenderHint(QPainter.RenderHint.Antialiasing)
## Draw snake
for x, y in self.snake:
painter.fillRect(x * CELL_SIZE, y * CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, Qt.GlobalColor.black)
## Draw food
painter.fillRect(self.food[0] * CELL_SIZE, self.food[1] * CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, FOOD_COLOR)
def keyPressEvent(self, event):
if event.key() == Qt.Key.Key_Up:
if self.direction != Qt.Key.Key_Down:
self.direction = Qt.Key.Key_Up
elif event.key() == Qt.Key.Key_Down:
if self.direction != Qt.Key.Key_Up:
self.direction = Qt.Key.Key_Down
elif event.key() == Qt.Key.Key_Left:
if self.direction != Qt.Key.Key_Right:
self.direction = Qt.Key.Key_Left
elif event.key() == Qt.Key.Key_Right:
if self.direction != Qt.Key.Key_Left:
self.direction = Qt.Key.Key_Right
def move_snake(self):
x, y = self.snake[0]
if self.direction == Qt.Key.Key_Up:
y -= 1
elif self.direction == Qt.Key.Key_Down:
y += 1
elif self.direction == Qt.Key.Key_Left:
x -= 1
elif self.direction == Qt.Key.Key_Right:
x += 1
if not self.is_valid_move(x, y):
self.timer.stop()
return
self.snake.insert(0, (x, y))
if (x, y) == self.food:
self.food = self.generate_food()
else:
self.snake.pop()
self.update()
def is_valid_move(self, x, y):
if x < 0 or x >= GRID_SIZE or y < 0 or y >= GRID_SIZE:
return False
if (x, y) in self.snake[1:]:
return False
return True
def generate_food(self):
import random
while True:
x = random.randint(0, GRID_SIZE - 1)
y = random.randint(0, GRID_SIZE - 1)
if (x, y) not in self.snake:
return x, y
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication([])
game = SnakeGame()
game.show()
app.exec()
代码注释
这是一个使用PyQt6库实现的贪吃蛇游戏的程序。下面是对程序的解释和注释:
from PyQt6.QtCore import Qt, QTimer
from PyQt6.QtGui import QColor, QPainter
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow
导入了PyQt6库的核心模块Qt、定时器模块QTimer,图形模块QColor和QPainter,以及窗口模块QApplication和QMainWindow。
CELL_SIZE = 30
GRID_SIZE = 20
SNAKE_INITIAL_LENGTH = 3
SNAKE_INITIAL_POSITION = (GRID_SIZE // 2, GRID_SIZE // 2)
SNAKE_INITIAL_DIRECTION = Qt.Key.Key_Right
FOOD_COLOR = QColor(0, 255, 0) ## 绿色
定义了一些常量,包括单元格大小CELL_SIZE,网格大小GRID_SIZE,蛇的初始长度SNAKE_INITIAL_LENGTH,蛇的初始位置SNAKE_INITIAL_POSITION,蛇的初始移动方向SNAKE_INITIAL_DIRECTION,以及食物的颜色FOOD_COLOR。
class SnakeGame(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("Snake Game")
self.setFixedSize(CELL_SIZE * GRID_SIZE, CELL_SIZE * GRID_SIZE)
self.snake = [(SNAKE_INITIAL_POSITION[0], SNAKE_INITIAL_POSITION[1] + i) for i in range(SNAKE_INITIAL_LENGTH)]
self.direction = SNAKE_INITIAL_DIRECTION
self.food = self.generate_food()
self.timer = QTimer()
self.timer.timeout.connect(self.move_snake)
self.timer.start(200) ## 蛇的移动速度
def paintEvent(self, event):
painter = QPainter(self)
painter.setRenderHint(QPainter.RenderHint.Antialiasing)
##绘制蛇
for x, y in self.snake:
painter.fillRect(x * CELL_SIZE, y * CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, Qt.GlobalColor.black)
## 绘制食物
painter.fillRect(self.food[0] * CELL_SIZE, self.food[1] * CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, FOOD_COLOR)
SnakeGame是一个继承自QMainWindow的类,表示整个游戏窗口。在初始化方法__init__中,设置了窗口标题和固定的窗口大小。初始化了蛇的初始位置、移动方向和食物,并创建了一个QTimer定时器,设置定时器的超时信号连接到move_snake方法上,并开始定时器。在paintEvent方法中,使用QPainter对象进行绘制,首先绘制蛇,然后绘制食物。
def keyPressEvent(self, event):
if event.key() == Qt.Key.Key_Up:
if self.direction != Qt.Key.Key_Down:
self.direction = Qt.Key.Key_Up
elif event.key() == Qt.Key.Key_Down:
if self.direction != Qt.Key.Key_Up:
self.direction = Qt.Key.Key_Down
elif event.key() == Qt.Key.Key_Left:
if self.direction != Qt.Key.Key_Right:
self.direction = Qt.Key.Key_Left
elif event.key() == Qt.Key.Key_Right:
if self.direction != Qt.Key.Key_Left:
self.direction = Qt.Key.Key_Right
在按键事件keyPressEvent中,根据按下的键盘按键修改蛇的移动方向。如果按下的是向上键并且当前方向不是向下,则将方向设为向上。类似地,如果按下的是向下、向左或向右键,并且当前方向不是相反方向,则更新蛇的移动方向。
def move_snake(self):
x, y = self.snake[0]
if self.direction == Qt.Key.Key_Up:
y -= 1
elif self.direction == Qt.Key.Key_Down:
y += 1
elif self.direction == Qt.Key.Key_Left:
x -= 1
elif self.direction == Qt.Key.Key_Right:
x += 1
if not self.is_valid_move(x, y):
self.timer.stop()
return
self.snake.insert(0, (x, y))
if (x, y) == self.food:
self.food = self.generate_food()
else:
self.snake.pop()
self.update()
move_snake方法用于更新蛇的位置。根据当前的移动方向,计算出蛇头的新坐标(x,
y)。然后检查新的坐标是否是有效的移动,如果无效,则停止定时器并返回。如果新坐标与食物的坐标相同,则表示蛇吃到了食物,将食物位置更新为新的随机位置,否则从蛇的尾部移除一个坐标。最后,调用update方法触发窗口的重绘。
def is_valid_move(self, x, y):
if x < 0 or x >= GRID_SIZE or y < 0 or y >= GRID_SIZE:
return False
if (x, y) in self.snake[1:]:
return False
return True
is_valid_move方法用于检查给定的坐标是否是有效的蛇的移动。如果坐标超出了网格范围,或者坐标在蛇的身体中已经存在,则返回False,否则返回True。
def generate_food(self):
import random
while True:
x = random.randint(0, GRID_SIZE - 1)
y = random.randint(0, GRID_SIZE - 1)
if (x, y) not in self.snake:
return x, y
generate_food方法用于生成食物的随机位置。使用random模块生成一个随机的x和y坐标,并检查该坐标是否在蛇的身体中。如果不在,则返回该坐标作为食物的位置。
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication([])
game = SnakeGame()
game.show()
app.exec()
在主程序中,创建一个QApplication对象app和SnakeGame对象game,然后显示游戏窗口,并开始应用程序的事件循环,以使窗口能够接收和处理事件。
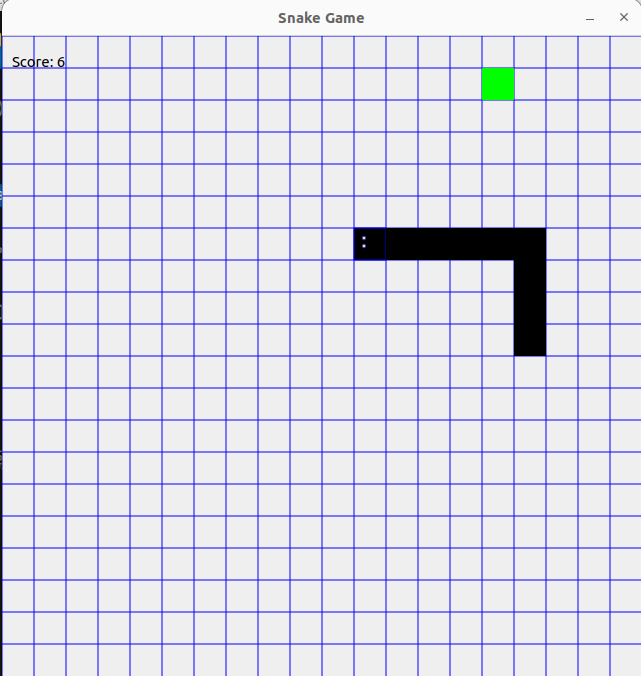
增加背景音乐,网格,计分
from PyQt6.QtCore import Qt, QTimer, QUrl
from PyQt6.QtGui import QColor, QPainter
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QLabel
from PyQt6.QtMultimedia import QMediaPlayer, QAudio, QAudioOutput
from PyQt6.QtMultimedia import QSoundEffect
CELL_SIZE = 30
GRID_SIZE = 20
SNAKE_INITIAL_LENGTH = 3
SNAKE_INITIAL_POSITION = (GRID_SIZE // 2, GRID_SIZE // 2)
SNAKE_INITIAL_DIRECTION = Qt.Key.Key_Right
FOOD_COLOR = QColor(0, 255, 0) ## Green color
class SnakeGame(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("Snake Game")
self.setFixedSize(CELL_SIZE * GRID_SIZE, CELL_SIZE * GRID_SIZE)
self.snake = [(SNAKE_INITIAL_POSITION[0], SNAKE_INITIAL_POSITION[1] + i) for i in range(SNAKE_INITIAL_LENGTH)]
self.direction = SNAKE_INITIAL_DIRECTION
self.food = self.generate_food()
self.score = 0
self.score_label = QLabel(self)
self.score_label.setGeometry(10, 10, 100, 30)
self.score_label.setText("Score: 0")
self.timer = QTimer()
self.timer.timeout.connect(self.move_snake)
self.timer.start(200) ## Snake movement speed
self.filename = "bg_music.mp3"
self.player = QMediaPlayer()
self.audio_output = QAudioOutput()
self.player.setAudioOutput(self.audio_output)
self.player.setSource(QUrl.fromLocalFile(self.filename))
self.audio_output.setVolume(50)
## 在音乐播放结束时重新开始播放
self.player.mediaStatusChanged.connect(self.on_music_status_changed)
## 开始播放背景音乐
self.player.play()
def on_music_status_changed(self, status):
if status == QMediaPlayer.MediaStatus.EndOfMedia:
self.player.setPosition(0) # 将音乐位置重置为0
self.player.play() # 重新播放背景音乐
def paintEvent(self, event):
painter = QPainter(self)
painter.setRenderHint(QPainter.RenderHint.Antialiasing)
## 绘制网格
painter.setPen(Qt.GlobalColor.blue) # 设置线条颜色为蓝色
for i in range(GRID_SIZE):
painter.drawLine(0, i * CELL_SIZE, self.width(), i * CELL_SIZE) ## 绘制水平线
painter.drawLine(i * CELL_SIZE, 0, i * CELL_SIZE, self.height()) ## 绘制垂直线
## 绘制蛇
for x, y in self.snake:
painter.fillRect(x * CELL_SIZE, y * CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, Qt.GlobalColor.black)
## 绘制食物
painter.fillRect(self.food[0] * CELL_SIZE, self.food[1] * CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, FOOD_COLOR)
def keyPressEvent(self, event):
if event.key() == Qt.Key.Key_Up:
if self.direction != Qt.Key.Key_Down:
self.direction = Qt.Key.Key_Up
elif event.key() == Qt.Key.Key_Down:
if self.direction != Qt.Key.Key_Up:
self.direction = Qt.Key.Key_Down
elif event.key() == Qt.Key.Key_Left:
if self.direction != Qt.Key.Key_Right:
self.direction = Qt.Key.Key_Left
elif event.key() == Qt.Key.Key_Right:
if self.direction != Qt.Key.Key_Left:
self.direction = Qt.Key.Key_Right
def move_snake(self):
x, y = self.snake[0]
if self.direction == Qt.Key.Key_Up:
y -= 1
elif self.direction == Qt.Key.Key_Down:
y += 1
elif self.direction == Qt.Key.Key_Left:
x -= 1
elif self.direction == Qt.Key.Key_Right:
x += 1
if not self.is_valid_move(x, y):
self.timer.stop()
return
self.snake.insert(0, (x, y))
if (x, y) == self.food:
self.score += 1
self.score_label.setText("Score: {}".format(self.score))
self.food = self.generate_food()
else:
self.snake.pop()
self.update()
def is_valid_move(self, x, y):
if x < 0 or x >= GRID_SIZE or y < 0 or y >= GRID_SIZE:
return False
if (x, y) in self.snake[1:]:
return False
return True
def generate_food(self):
import random
while True:
x = random.randint(0, GRID_SIZE - 1)
y = random.randint(0, GRID_SIZE - 1)
if (x, y) not in self.snake:
return x, y
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication([])
app.setStyle("fusion") # 使用Fusion样式,确保网格线条显示正常
game = SnakeGame()
game.show()
app.exec()



